The COVID-19 pandemic, a global crisis of unparalleled proportions, has not only reshaped our lives but also sent shockwaves through the world’s economies. As nations grappled with the spread of the virus, industries that form the backbone of our societies faced extraordinary challenges, forcing them to adapt, innovate, and, in some cases, fight for survival.
What industries suffered the most?
The level of impact of COVID-19 depends on a myriad of factors, including government responses, vaccination rates, and the duration of the pandemic. Here’s a more detailed examination of the industries most affected by the pandemic:
Travel and Tourism
This sector bore the brunt of the pandemic’s economic impact. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and the fear of contagion led to a dramatic decline in global travel. Airlines grounded fleets, hotels faced empty rooms, and tourist destinations emptied. Losses in this sector were staggering, affecting millions of jobs and businesses.
Hospitality and Restaurants
Lockdowns and restrictions on indoor dining led to reduced foot traffic, significant revenue losses, and widespread layoffs. Many businesses in this sector had to pivot to takeout and delivery services or temporarily shut their doors.
Retail
Brick-and-mortar retail stores faced challenges as consumers shifted to online shopping amid health concerns. Many retailers had to quickly adapt their business models to e-commerce or navigate temporary closures. The pandemic accelerated the digitization of the retail industry.
Entertainment and Events
The entertainment industry saw closures and cancellations across various segments, including theaters, concerts, sports events, and festivals.

Manufacturing and Supply Chains
Manufacturing industries experienced disruptions due to factory closures, workforce reductions, and supply chain interruptions. Global supply chains faced delays, impacting the production and distribution of goods. Businesses reconsidered their supply chain strategies for resilience.
Oil and Energy
Reduced travel and economic activity led to a significant drop in oil demand, plummeting oil prices. Energy companies, including oil and gas producers, faced financial challenges. Renewable energy projects also faced delays and setbacks.
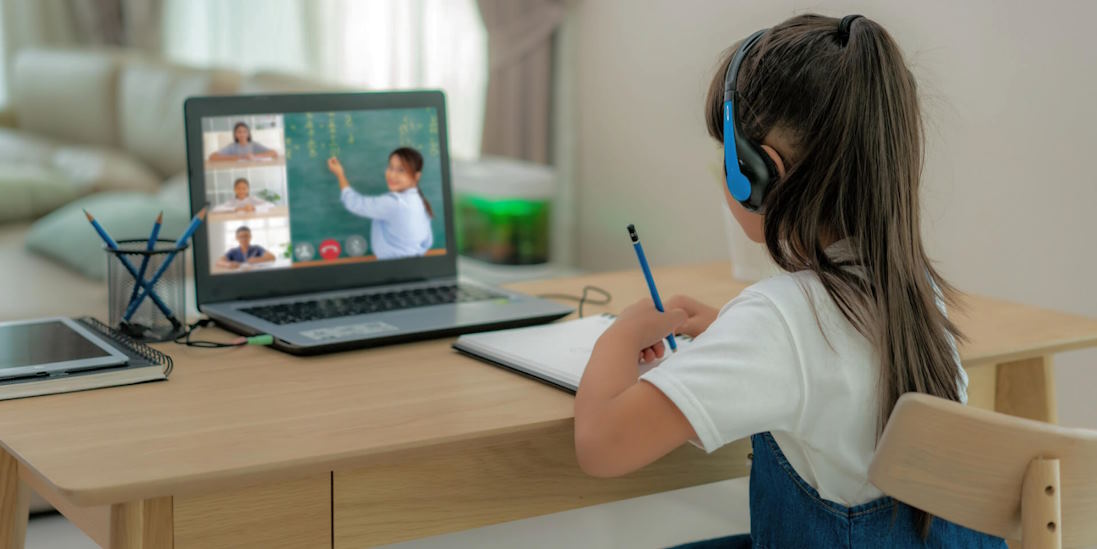
Education
Educational institutions had to adapt rapidly to the challenges of remote learning. Students and educators grappled with the transition, highlighting access, equity, and digital literacy issues in education. The pandemic underscored the need for innovation in the education sector.
Aviation
Airlines experienced a drastic reduction in passengers and revenue as international and domestic travel restrictions were imposed. Some airlines faced financial difficulties and were forced to reduce operations or seek government support.
Small Businesses
Small businesses across diverse sectors, including retail, hospitality, and services, were particularly vulnerable. Many struggled to adapt to changing consumer behaviors and navigate economic uncertainties.
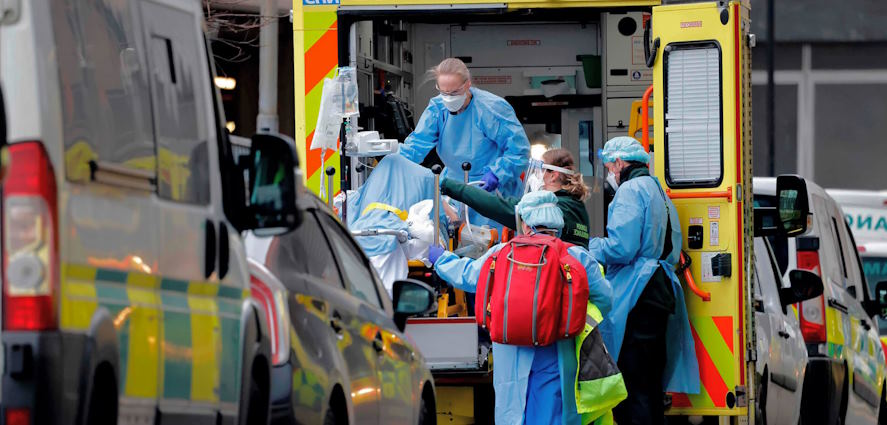
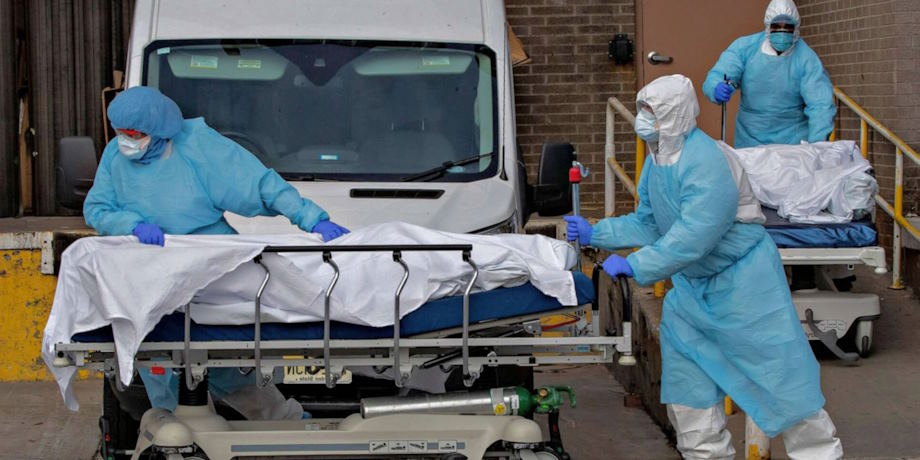
Healthcare
The healthcare industry played a pivotal role in responding to the pandemic, but it also faced challenges. Hospitals and healthcare facilities were overwhelmed by COVID-19 patients. Elective procedures were postponed, impacting hospital revenues.
Transportation
Public transportation systems, including buses, subways, and commuter trains, significantly decreased ridership as people worked from home and limited non-essential travel. Revenue losses posed financial challenges for transit agencies.